How to Design a Wiring Harness: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide for Engineers and DIYers
Introduction: The Backbone of Electrical Systems
A well-designed wiring harness is the central nervous system of any electrical application, from custom cars and motorcycles to industrial machinery and smart appliances. Whether you're an electrical engineer tackling a complex project or a DIY enthusiast restoring a classic vehicle, understanding how to design a wiring harness is crucial for reliability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide walks you through the entire process, from initial concept to finished product.
Phase 1: Planning & Requirements Analysis (Wiring Harness Design Planning)
1.1 Define the System Requirements
Before drawing a single line, answer these critical questions:
. Application & Environment: Is it for an automotive, marine, aerospace, or industrial application? What are the temperature ranges, exposure to moisture, chemicals, or vibration?
. Electrical Load Analysis: List every component (actuators, sensors, lights, ECUs). Determine each one's:
> Voltage (e.g., 12V DC, 24V DC, 110/220V AC)
> Current Draw (Amperes) - Crucial for wire gauge selection.
> Duty Cycle (continuous or intermittent use).
. Circuit Protection: Plan fuses, circuit breakers, or relays for each circuit. The protection device rating should be slightly above the circuit's normal operating current but below the wire's ampacity.
. Connector Strategy: Choose connectors based on pin count, environmental sealing (IP rating), locking mechanism, and compatibility with components.
. Regulations & Standards: Identify relevant standards (e.g., SAE, ISO, UL, MIL-SPEC) for your industry.
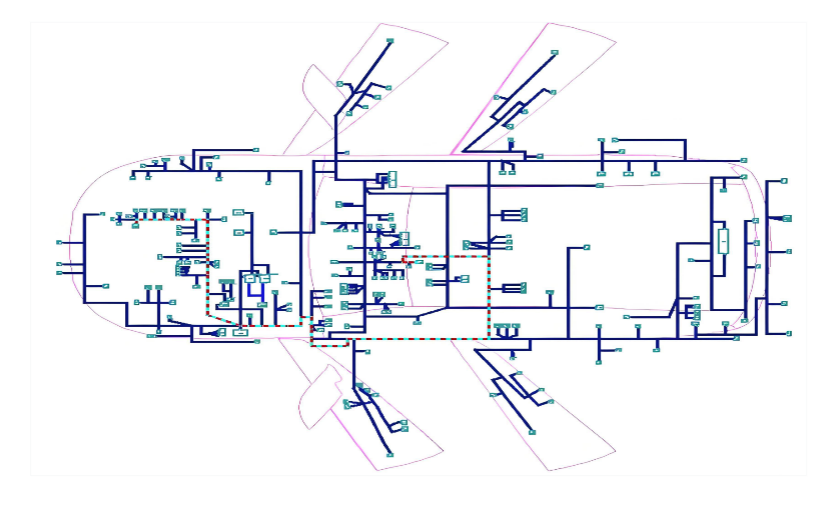
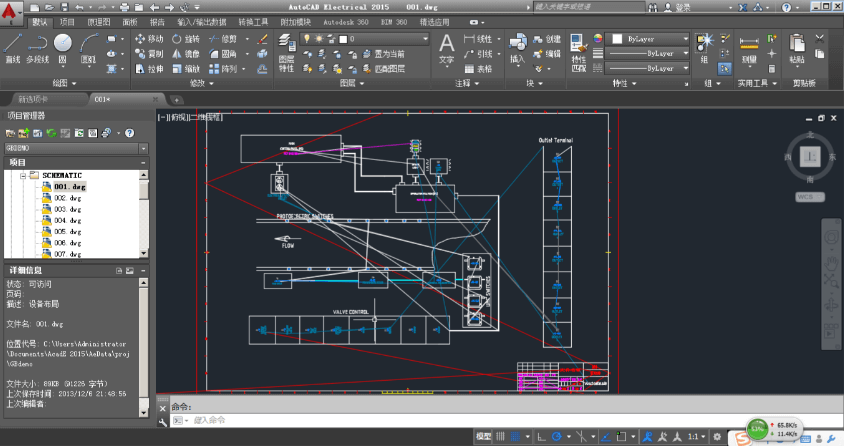
1.2 Create the Schematic Diagram
The schematic is the logical blueprint of your electrical system.
. Use Professional Software: Tools like KiCad EDA, AutoCAD Electrical, SolidWorks Electrical, or even Visio are invaluable.
. Best Practices:
> Use clear and consistent symbols.
> Label every wire with a unique identifier (Wire ID) or color code.
> Clearly mark connector pinouts, component terminals, and ground points.
> Group related circuits (e.g., all lighting, all engine sensors) logically.
Phase 2: Detailed Design & Component Selection
2.1 Wire Selection: The Lifelines of Your Harness
Choosing the right wire is fundamental to safety and function.
. Wire Gauge (AWG): Based on current draw and wire length. Use an American Wire Gauge (AWG) chart. Longer runs or higher currents require thicker wire (lower AWG number) to minimize voltage drop.
. Insulation Type:
> PVC: General purpose, flexible, cost-effective.
> Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Superior heat and abrasion resistance.
> PTFE (Teflon): Excellent for extreme high temperatures and chemical resistance.
> Specifications: Look for industry grades like SAE J1128 (auto), UL 1426 (marine), or MIL-W-22759 (aerospace).
. Color Coding: Develop a consistent scheme (e.g., red for +12V constant, black for ground, yellow for switched power, green for sensor signals). Use tracer stripes for more variations.
2.2 Connector & Terminal Selection
. Types: Deutsch, Molex, TE Connectivity (AMP), JST, etc.
. Key Factors: Current rating, environmental sealing (check IP ratings), vibration resistance, and proper crimp tool availability.
. Pro Tip: Minimize connector types to reduce tooling and assembly complexity.
2.3 Protection & Routing Design
. Conduit & Sleeving:
> Braided Loom: Excellent abrasion resistance, flexible.
> Corrugated Conduit: Good all-around protection, easy to route wires into.
> Heat-Shrink Tubing: For sealing splices, connectors, and ends.
> Spiral Wrap: Easy to install and modify, great for prototypes.
. Routing Path: Design the harness to follow the natural contours of the vehicle or chassis. Avoid sharp edges, hot surfaces, and moving parts. Plan service loops for strain relief and future servicing.
. Secure Mounting: Select appropriate clips, P-clamps, cable ties, and adhesive mounts. Follow the rule: "A clamp or tie every 12-18 inches and within 3 inches of every connector."
Phase 3: Documentation & Prototyping
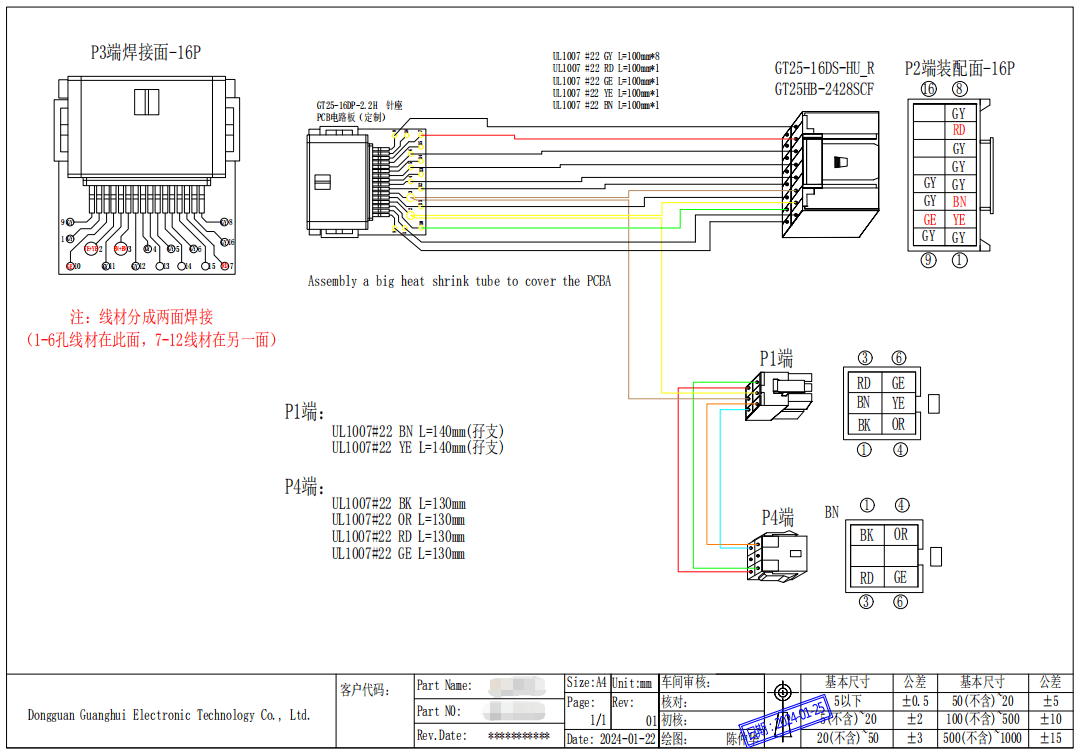
3.1 Create Manufacturing Documents
. Harness Assembly Drawing: A 2D or 3D drawing showing the physical layout, branch points, lengths, connector locations, and clamp positions.
. Bill of Materials (BOM): A detailed list of every part: wires (gauge, color, length), connectors, pins, seals, sleeves, clamps, etc.
. Cut List: A simple list for the assembler specifying each wire segment by its ID, color, gauge, and cut length.
3.2 Build a Prototype (Beta Harness)
. Hand-build the first harness using your drawings and BOM.
. Purpose: Test for fitment, length accuracy, connector accessibility, and overall routing. This is cheaper than making production tooling only to find a major flaw.
. "Breadboard" the Electrical System: Connect the prototype harness to the actual components on a bench and test all functions.
Phase 4: Testing & Validation (Wiring Harness Testing)
Never skip rigorous testing. A fault here can cause system failure or fire.
. Continuity Test: Verify every wire makes connection from end-to-end.
. Short Circuit Test: Ensure no two wires that shouldn't be connected are touching.
. Hi-Pot (Dielectric Withstanding Voltage) Test: For high-voltage applications (e.g., EVs), tests the insulation's ability to withstand high voltage without breaking down.
. Insulation Resistance Test: Measures the quality of the insulation.
. Pull Test: Mechanically tests the strength of crimped terminal connections.
. In-System Functional Test: Install the harness in the final application and test under real-world operating conditions (vibration, heat, etc.).
Essential Tools for Wiring Harness Design & Assembly
. Design: CAD software, schematic capture tools.
. Assembly:
> Wire Stripper & Cutter (precision manual or automatic machine)
> Crimping Tool: Invest in a high-quality, ratcheting, calibrated crimper specific to your terminal series. This is the most important tool for reliability.
> Heat Gun for shrink tubing.
> Multimeter for testing.
> Terminal Removal Tools (for fixing mistakes).
Common Design Mistakes to Avoid
1. Ignoring Voltage Drop: Using wire too thin for long runs, causing components to underperform.
2. Poor Strain Relief: Wires pulling directly on connector solder joints or terminals.
3. Inadequate Protection: Running wires through areas without proper sleeving against abrasion.
4. Forgetting Serviceability: Designing a harness that is impossible to install or remove without disassembling major components.
5. Skipping the Prototype: Going straight to mass production is a recipe for costly errors.
Conclusion: From Design to Reality
Designing a wiring harness is a meticulous process that blends electrical engineering with mechanical packaging. By following these structured phases—thorough planning, careful component selection, detailed documentation, prototyping, and rigorous testing—you can create a harness that is safe, reliable, and manufacturable.
Whether you're designing a single custom harness or developing one for production, the principles remain the same. Start with a clear plan, respect the electrical and physical requirements of the environment, and never compromise on the quality of materials and terminations. A great wiring harness design is one you never have to think about again—it just works.
Ready to start your project?
Dongguan Guanghui Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in wire harnesses and cable assemblies, with more than 19 years of R&D experience. We can provide better economic solutions and innovative wiring harnesses for many industries, such as automotive, machinery, medical, electrical, communications and other cable assemblies. With the support of R&D engineering, we focus on turnkey solutions. Support OEM/ODM.
We have a complete and advanced APQP R&D system, and all processes follow the IPC620 standard. Our advantage is to quickly provide high-quality solutions and professional services for production enterprises.
Welcome to contact with us!